The intersection of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly emerging as a catalyst for the emergence of new industries, innovative technologies, and heightened productivity and efficiency across established sectors. As the realm of AI within robotics progresses, its tangible applications in the real world are becoming more evident.
AI is crucially reshaping industries and enhancing daily life, from self-driving cars, customer service, and healthcare to industrial and service robots.
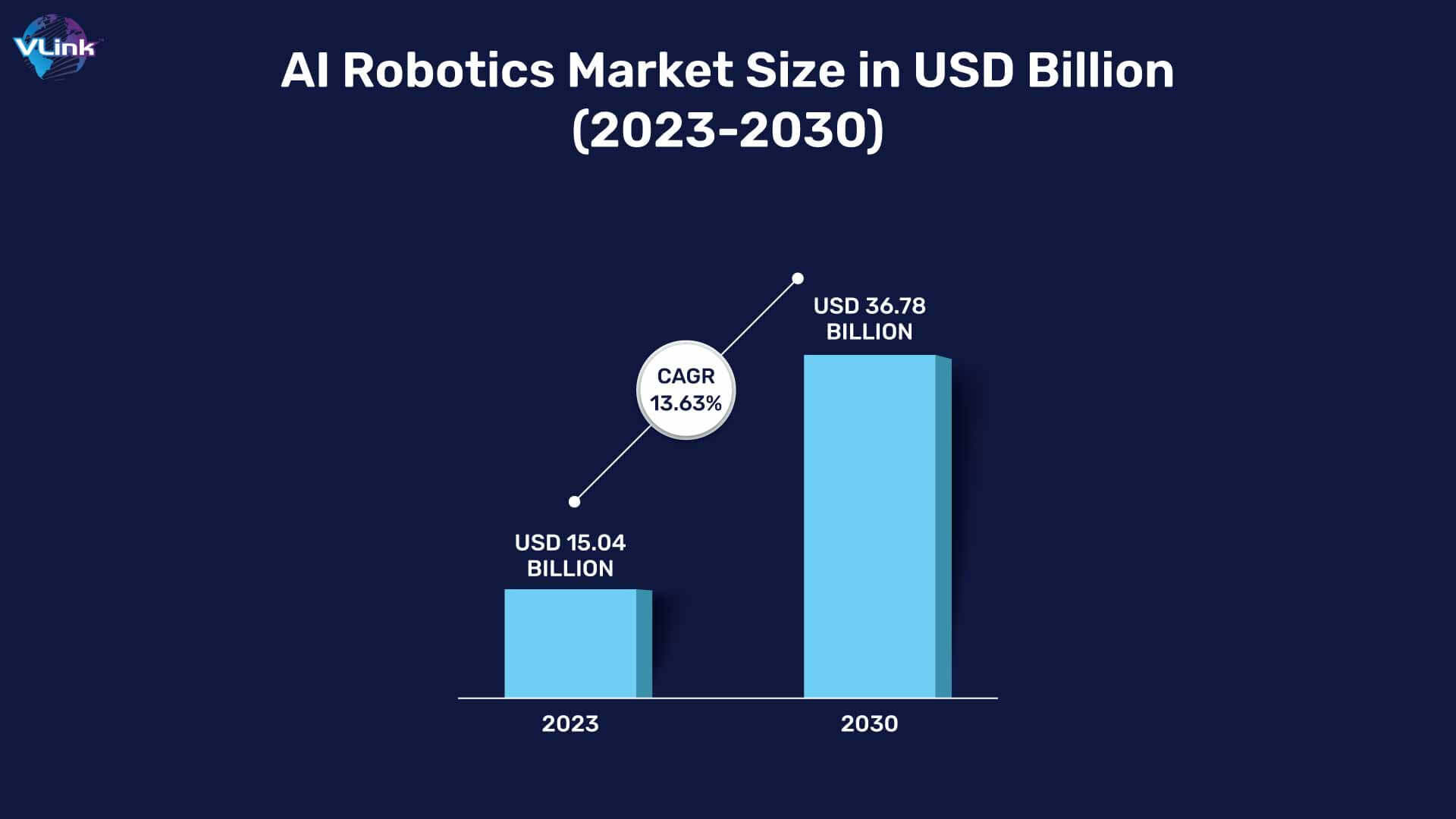
This growth presents an opportunity for business owners who want to invest in AI-enabled chatbot development solutions.
This blog will explore why Artificial Intelligence plays a vital role in robotic technology.
Let's start with AI in robotic technology:
What is AI in Robotic Technology?
AI in robotic technology refers to integrating artificial intelligence to enhance the capabilities of robots. It enables robots to perceive, learn, and adapt to their environment, improving navigation, object recognition, and decision-making tasks. This interaction between AI and robotics drives automation, efficiency, and autonomy advancements.
Are Robotics and Artificial Intelligence the Same Thing?
No, robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) are not the same thing, but they are closely related fields. Robotics is a broader discipline encompassing robots' design, construction, operation, and use. Robots are physical devices or machines programmed to perform specific tasks, often focusing on automation and interaction with the physical world.
On the other hand, artificial intelligence refers to developing algorithms and computer systems to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI enables machines to learn from data, make decisions, and solve problems. While AI can be applied to various domains beyond robotics, integrating AI into robotics enhances the capabilities of robots.
In robotics, AI is often used to imbue robots with the ability to perceive their environment, make decisions based on that perception, and adapt to changing circumstances. This combination of robotics and AI is potent, allowing robots to operate autonomously, learn from experience, and execute complex tasks with flexibility and intelligence.
How is AI Used in Robotic Technology?
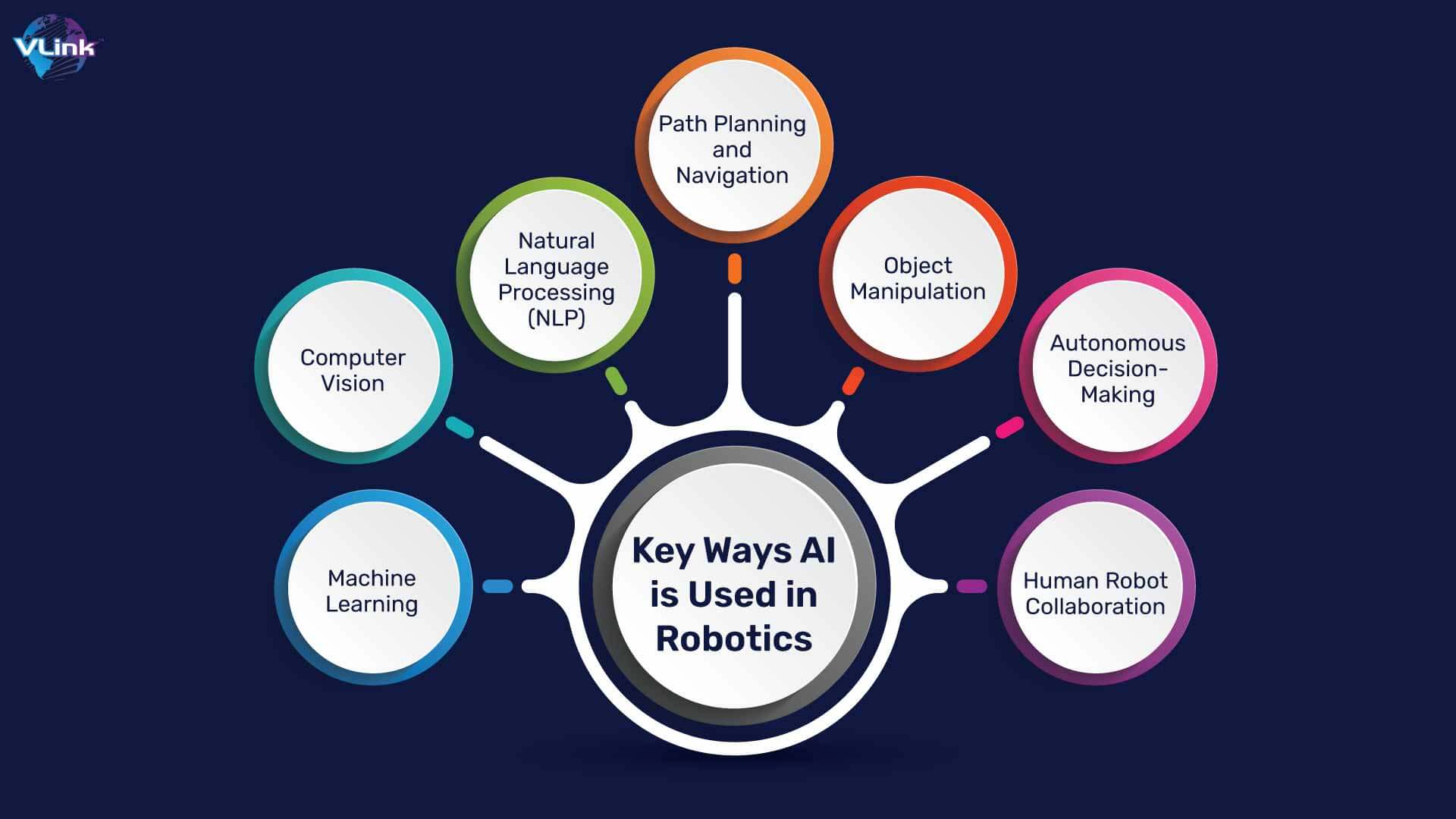
Here are different keyways AI is applied in robotic process automation:
Machine Learning
AI algorithms empower robots to enhance performance by learning from data and experiences. This capability is essential for tasks requiring pattern recognition, such as object detection, navigation, and grasping, enabling robots to improve their abilities over time continually.
Computer Vision
Robots leverage AI-powered computer vision to interpret and comprehend visual information in their environment. This capability is essential for recognizing objects, people, and obstacles, empowering robots to navigate and interact effectively with their surroundings.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Integrating NLP enables robots to comprehend and respond to human commands and inquiries. It enhances their usability in human-robot interaction scenarios and makes them more user-friendly.
Path Planning and Navigation
AI algorithms support robots in devising optimal paths and navigating intricate environments. It entails making real-time decisions to avoid obstacles and efficiently achieve destinations.
Object Manipulation
AI algorithms enhance the finesse of robots by enabling precise control of robotic arms and grippers. This capability is crucial for assembly, sorting, and handling delicate objects.
Autonomous Decision-Making
AI enables robots to make decisions autonomously based on information gathered from their environment. This autonomy is essential for robots to adapt to dynamic situations without requiring continual human intervention.
Human-Robot Collaboration
AI enables secure and efficient collaboration between humans and robots, encompassing the recognition of human gestures, comprehension of intentions, and the subsequent adjustment of the robot's behavior in response.
In conclusion, incorporating AI into robotics elevates robots' abilities, rendering them more intelligent, flexible, and proficient in executing various tasks across various environments.
Actual Use Cases of AI Technologies for Robotics
Use Case: AI is utilized in the navigation systems of autonomous vehicles and drones.
How AI is Used: Machine learning algorithms empower these vehicles to analyze sensor data from cameras and LIDAR, allowing them to make instantaneous decisions regarding their surroundings. AI is crucial in path planning, obstacle avoidance, and adjusting to dynamic scenarios.
Use Case: Surgical robots and robotics.
How AI is Used: In surgical robotics, AI supports precise movements and decision-making throughout surgical procedures. Additionally, machine learning algorithms find application in analyzing medical data, contributing to diagnosis and treatment planning. Robotics leverage AI to comprehend and react to user movements and the environment.
Use Case: AI in precision farming and autonomous tractors.
How AI is Used: AI algorithms analyze data from sensors and satellite imagery to optimize planting, irrigation, and harvesting. Autonomous tractors use AI for navigation and decision-making in the field, improving crop yield and resource efficiency.
Use Case: AI-driven robotics in manufacturing and logistics.
How AI is Used: Robots equipped with computer vision and machine learning can recognize and handle objects of varying shapes and sizes. They can optimize tasks like picking and placing items, assembly, and quality control. AI helps robots adapt to changes on the production line and improve efficiency.
Use Case: AI-enhanced robots for disaster response.
How AI is Used: Robots with AI algorithms can navigate complex and dynamic environments during search and rescue missions. Computer vision helps identify and assess the surroundings, while machine learning enables the robot to adapt its actions based on the changing conditions and information received.
4 Applications of AI-Driven Robotics
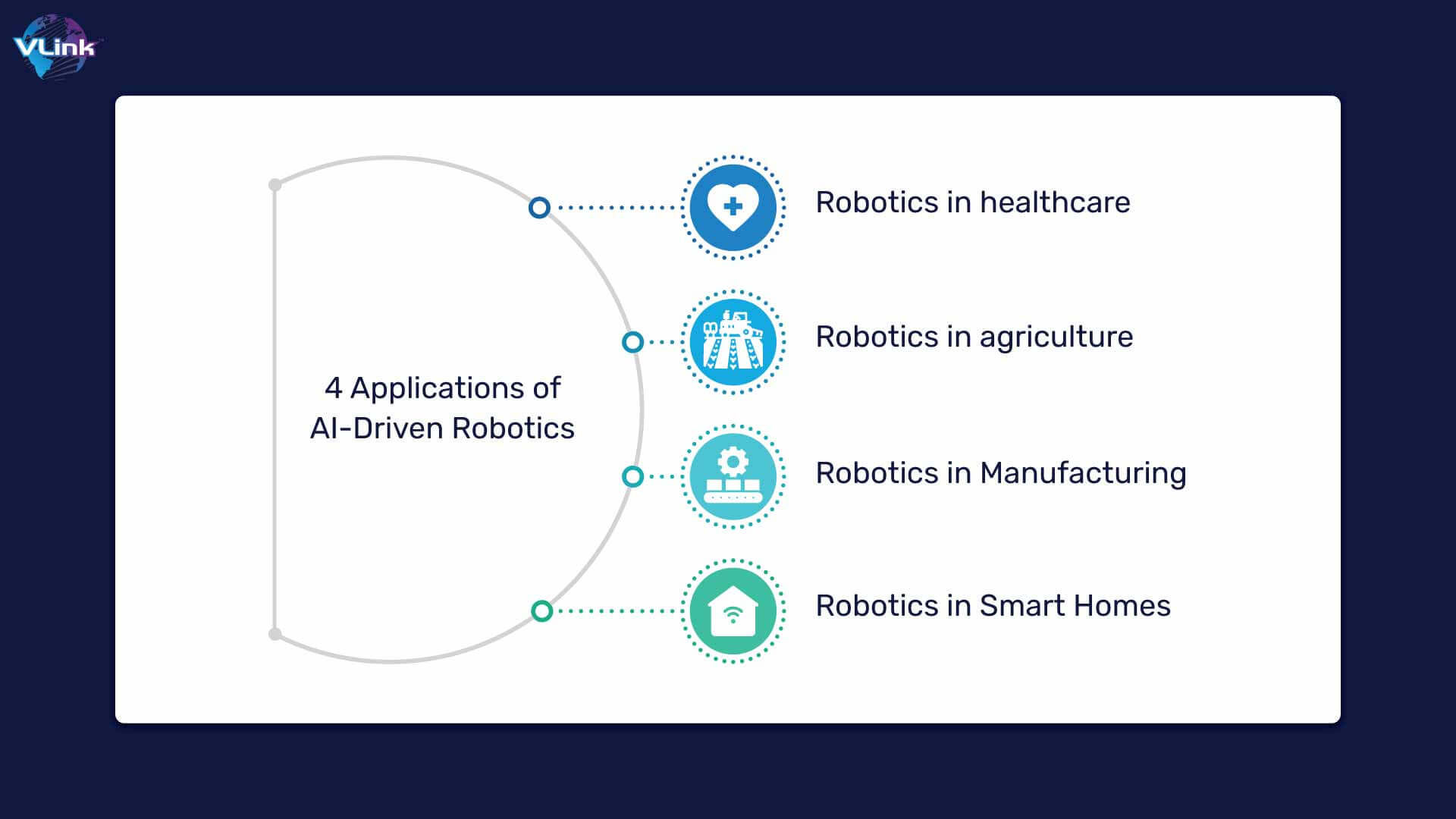
Whether utilized in autonomous blood drawing devices or robotic arms performing surgeries, robotics plays a vital role in addressing healthcare challenges that human employees may find challenging.
Integrating robotics in healthcare industry enhances efficiency and elevates the standard of patient care, creating a secure environment for both healthcare providers and patients.
In healthcare settings, service robots are valuable for transporting linens and supplies, mainly when workers risk pathogen exposure. The prevalence of hospital-acquired infections is a significant concern, with 1 in 25 US hospital patients diagnosed with at least one disorder annually.
Robots designed for cleaning and disinfection not only minimize exposure risks but also contribute to reducing the incidence of these infections.
Utilizing robotics in agriculture has the potential to address labor shortages and alleviate worker fatigue while contributing to sustainability efforts. It involves systematically monitoring plant conditions, including nutrients, water, and sunlight, to optimize the growth of crops.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence enables the efficient use of resources, reducing waste and conserving water. By employing robots for monotonous and time-consuming tasks, such as monitoring plant levels, the agricultural sector can benefit from increased efficiency and improved yields in successive harvests.
- Utility platforms
- Phenotyping
- Harvest and picking
- Sorting and packing
- Weed control
- Autonomous pruning, mowing, thinning, seeding, and spraying
Here are applications of robotics in manufacturing industry:
Material Handling
Material handling applications in robotics involve transporting materials or parts between different locations, encompassing tasks such as machine loading, unloading, and material transfer.
These tasks range from straightforward activities, like moving apart from one conveyor to another, to more intricate processes, such as arranging details based on calculations performed by the robot.
For robots engaged in loading and unloading parts, the inclusion of a gripper is essential. The gripper must be meticulously designed to match the geometry of the features, ensuring a secure and precise grasp during the handling process.
Processing operations
Robots are utilized to operate various tools for executing workpiece processes, including tasks such as spot welding, arc welding, spray painting, and more. In the United States, one prevalent industrial application of robots involves spot welding in the assembly of automobile bodies.
Additionally, robots are employed in operations such as polishing, grinding, routing, and manipulating tools to achieve desired outcomes.
In spot welding, the robot strategically places the welder against the frames and panels of automobiles, contributing to the assembly of a fundamental car body.
In the case of arc welding, robots engage in a continuous process, guiding the welding rod along the seam to accomplish the welding task. For spray painting, robots precisely handle a spray-painting gun, coating surfaces, and objects with paint to achieve a uniform and efficient finish.
Assembly and inspection
The rising prevalence of robots in assembly and inspection stems from their cost-effectiveness compared to manual labor. In assembly tasks, robots are programmed to produce multiple product styles in batches, undergoing reprogramming between each set.
An alternative method involves various product styles manufactured within the same assembly cell. In this approach, each robot can identify the product style as it arrives and perform the required task for that particular unit.
In addition, robots equipped with sensors can assume the role of inspecting work parts, serving as a replacement for human labor in scenarios where:
- Repetitive operations that involve the same basic movements every cycle.
- Operations are dangerous or uncomfortable for workers.
- Activities need work tools that are difficult or heavy to manage.
- Operations allow robots to be used in two or three ways.
Here are some specific areas where robotics plays a crucial role in smart home environments:
Home Cleaning:
- Robotic Vacuum Cleaners
- Robotic Mops
Security and Surveillance:
- Security Robots
- Surveillance Drones
Personal Assistance:
- Smart Speakers with Voice Assistants and AI personal assistant app
- Social Robots
- Integrate Chatbot into your website
Environmental Monitoring:
- Robotic Sensors: Robots with sensors monitor environmental conditions such as air quality, temperature, and humidity.
Harness the Power for AI-Enabled Chatbots with VLink!
Leverage the potential of AI-enabled chatbots with VLink! Our cutting-edge platform combines natural language processing and machine learning, providing seamless communication and enhanced user experiences.
We specialize in delivering machine learning and AI development services. Our experts create highly intelligent and adaptable AI chatbots with the power to redefine internal and customer interactions for businesses.
Whether you want to automate tasks, offer 24/7 customer support, or deliver specialized responses to user queries, our dedicated team will deliver chatbots that are adept at excelling in a range of functions. They serve as a versatile solution to meet your diverse business requirements.









 Shivisha Patel
Shivisha Patel

















