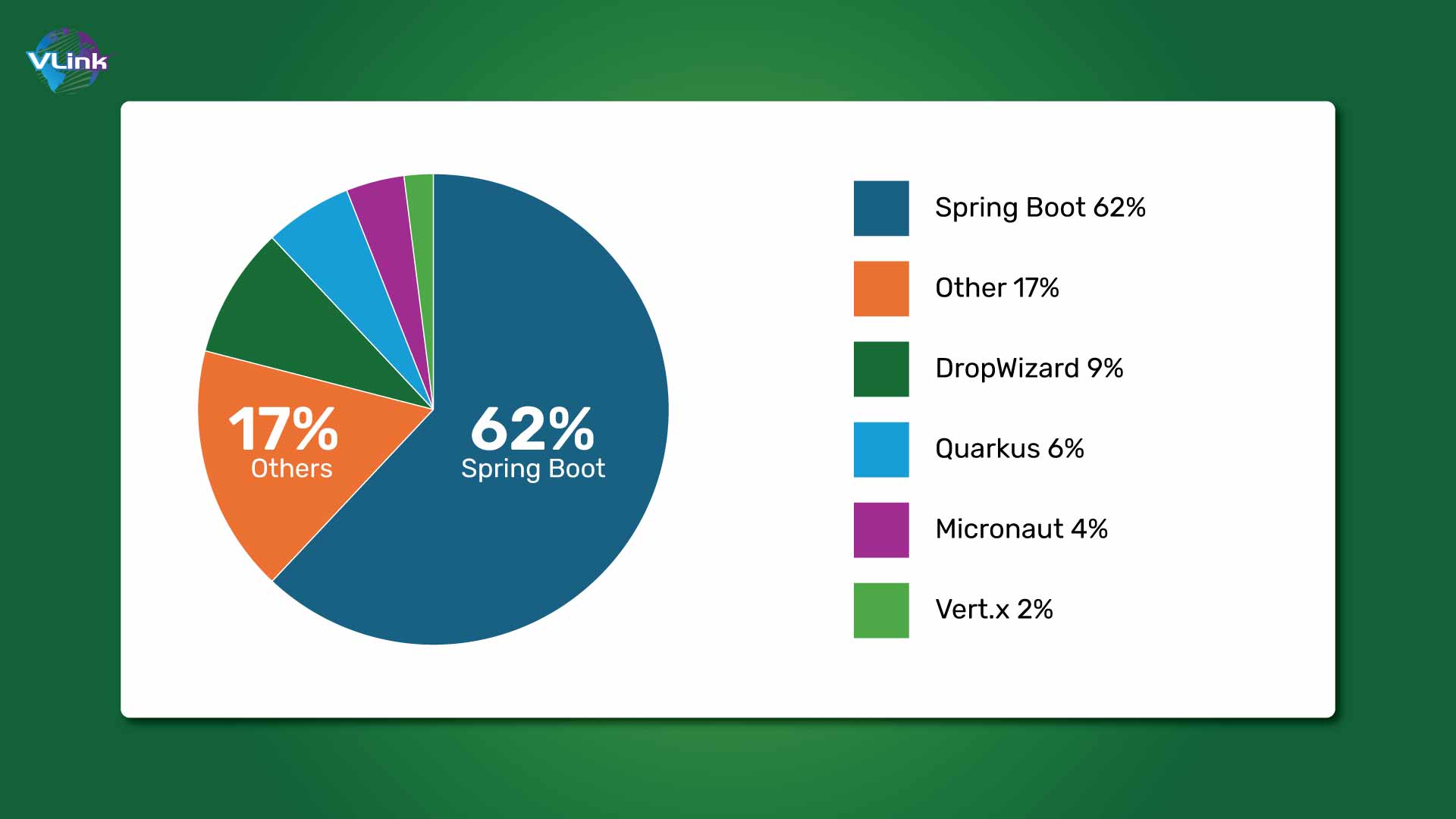
Spring is one of the most popular Java Frameworks when it comes to creating robust web applications. Spring Boot and Spring MVC are two most significant modules of Spring Framework. They are powerful tools, each with its pros, cons, features, and use cases. It could be challenging to find the right frameworks for robust Java development.
If you want to choose the right frameworks between Spring Boot and Spring MVC, read this blog.
What is Spring MVC?
Spring MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a Spring Framework module for creating robust and flexible web apps. It comes with basic features of the core Spring framework including Dependency Injection and Inversion of Control.
The MVC pattern differentiates software's different factors, such as input logic, business logic, and UI logic, while providing a loose coupling between them.
How Does Spring MVC Work?
Spring MVC works by routing incoming HTTP requests to appropriate controllers, which handle the requests and prepare a response. Controllers interact with services and repositories to process data and invoke appropriate views to generate the response sent back to the client.
Spring MVC Features
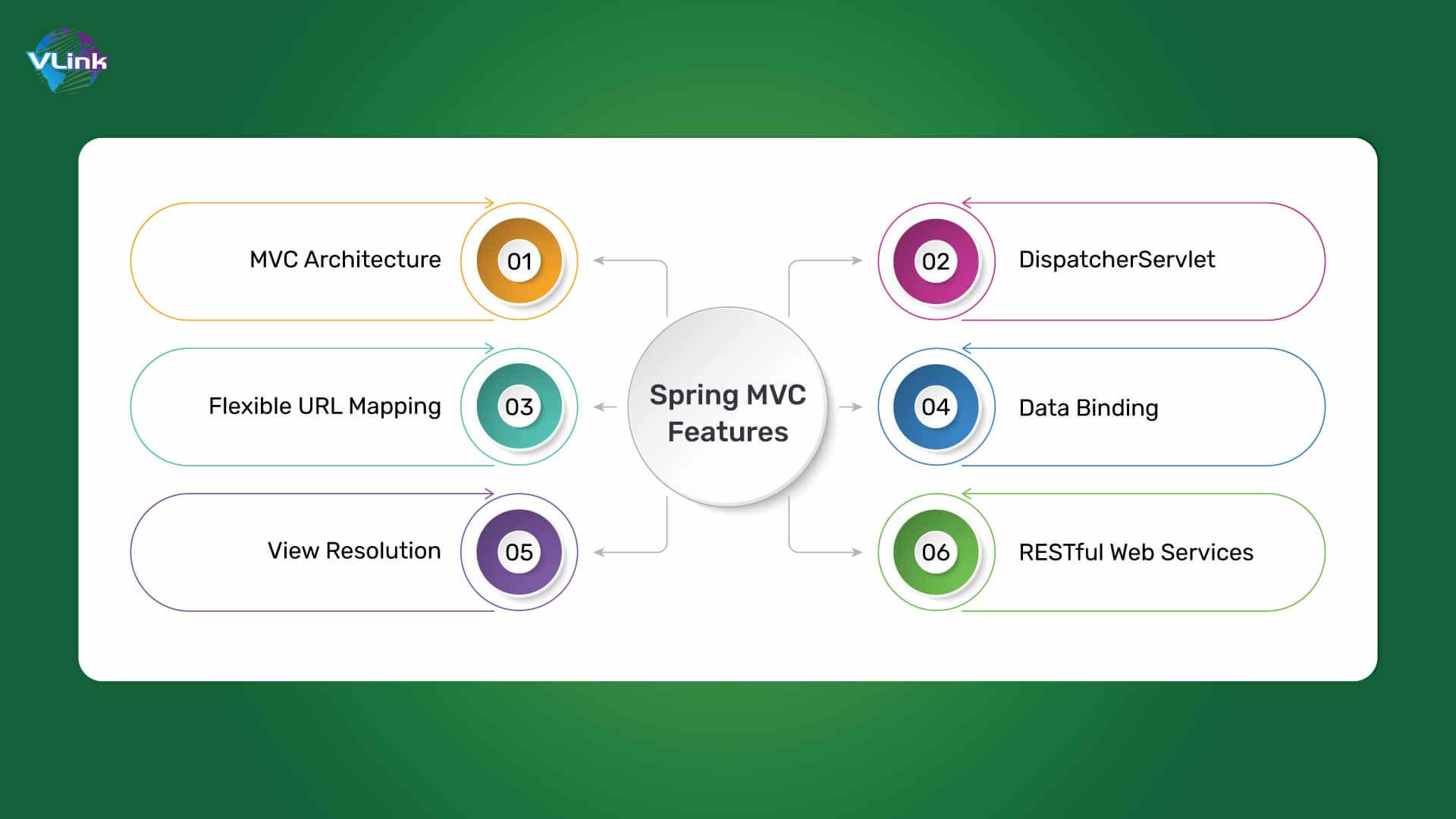
MVC Architecture
Spring MVC follows the Model-View-Controller architectural pattern. It separates software into three interconnected elements:
Model (Data and business logic)
View (Presentation layer)
Controller (Request handling and application flow)
DispatcherServlet
As a main component of Spring MVC, DispatcherServlet is responsible for stopping and routing incoming HTTP requests to the proper controller based on URL mappings.
Flexible URL Mapping
It allows programmers to define URL mappings flexibly, making it easy to route requests to specific controllers and techniques.
Data Binding
Thanks to powerful data binding capabilities, Spring MVC allows automatic conversion between HTTP request parameters and Java objects, simplifying form handling and validation.
View Resolution
Spring MVC supports several view technologies, such as JavaServer Pages (JSP), Thymeleaf, and FreeMarker. It enables developers to select the view technology that best suits their requirements.
RESTful Web Services
Spring MVC is mainly used for traditional web app development. But, it is also useful for building RESTful web services by leveraging its capabilities for request handling and data binding.
Spring MVC: Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
Robust Architecture | Steep Learning Curve |
Flexible | Overhead |
Extensive Ecosystem |
|
Customization |
|
What is Spring Boot?
Spring Boot is an alternative to Spring MVC that offers preconfigured setup for rapid app development. It allows programmers to focus on growth instead of the complexities of configuration.
Spring Boot software can operate independently without any need for an external web server.
How Does Spring Boot Work?
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration, integrated servers, and opinionated defaults to simplify Spring app development services. This framework automatically configures common elements as per classpath and dependencies, minimizing manual setup. Java developers must focus on writing application logic rather than configuring infrastructure.
Spring Boot Features
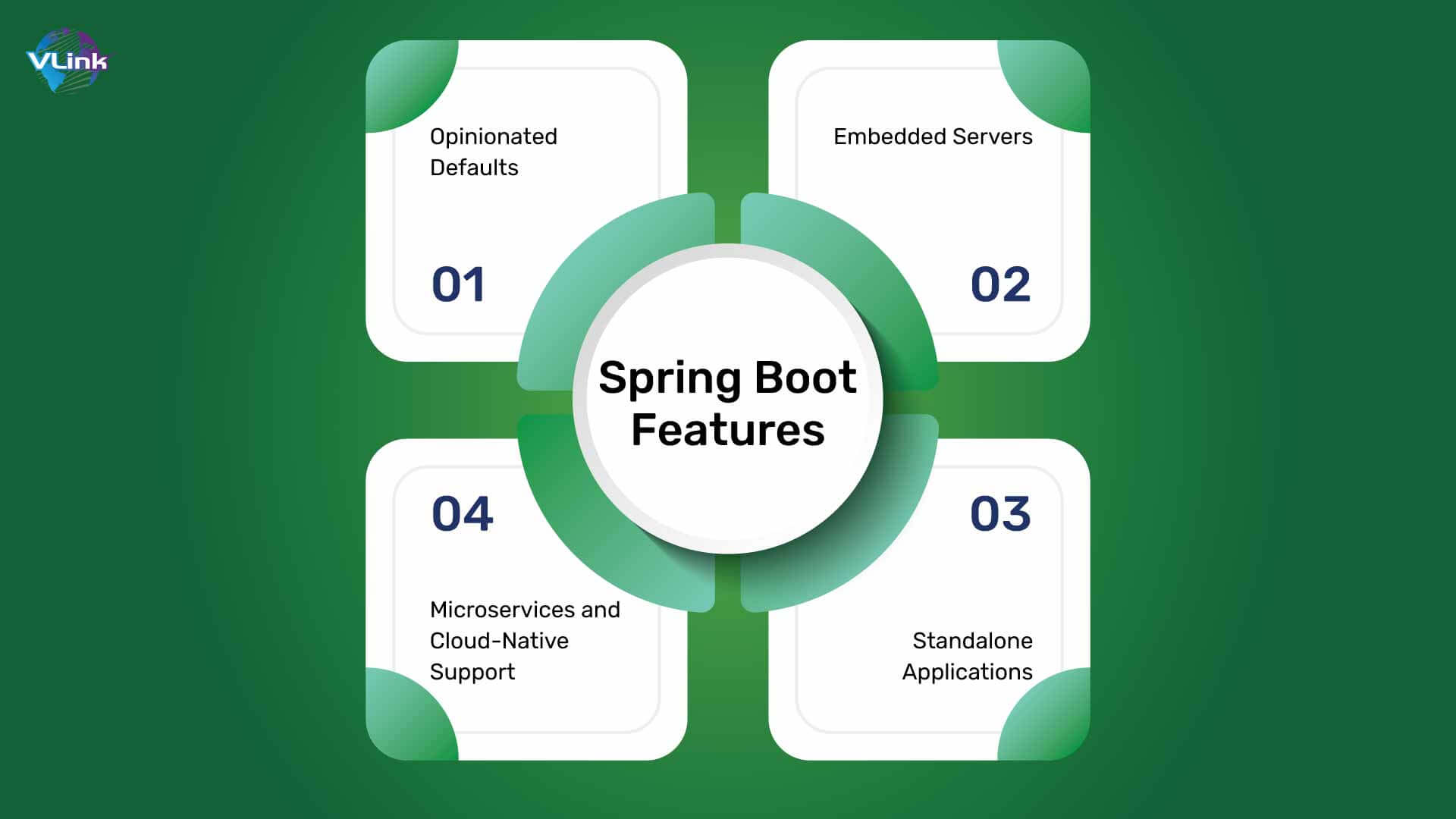
Opinionated Defaults
Spring Boot supports default configurations and settings for several aspects of software development. This opinionated method minimizes the need for extensive manual configuration, allowing programmers to get started quickly.
Embedded Servers
Spring Boot reduces the need for manual server setup and configuration thanks to its integrated servlet containers like Tomcat, Jetty, and Undertow.
Standalone Applications
Spring Boot applications can be operated as standalone JAR files. They come with embedded servers, making deployment easy.
Microservices and Cloud-Native Support
Spring Boot is ideal for microservices and cloud-native app development. This framework provides features like service discovery, load balancing, and externalized configuration for microservices architectures.
Spring Boot: Pros & Cons
Pros | Cons |
Rapid development | Complexity |
Large ecosystem | Limited flexibility |
Embedded servers |
|
Convention over configuration |
|
Spring MVC Vs. Spring Boot: Which One Is a Better Framework
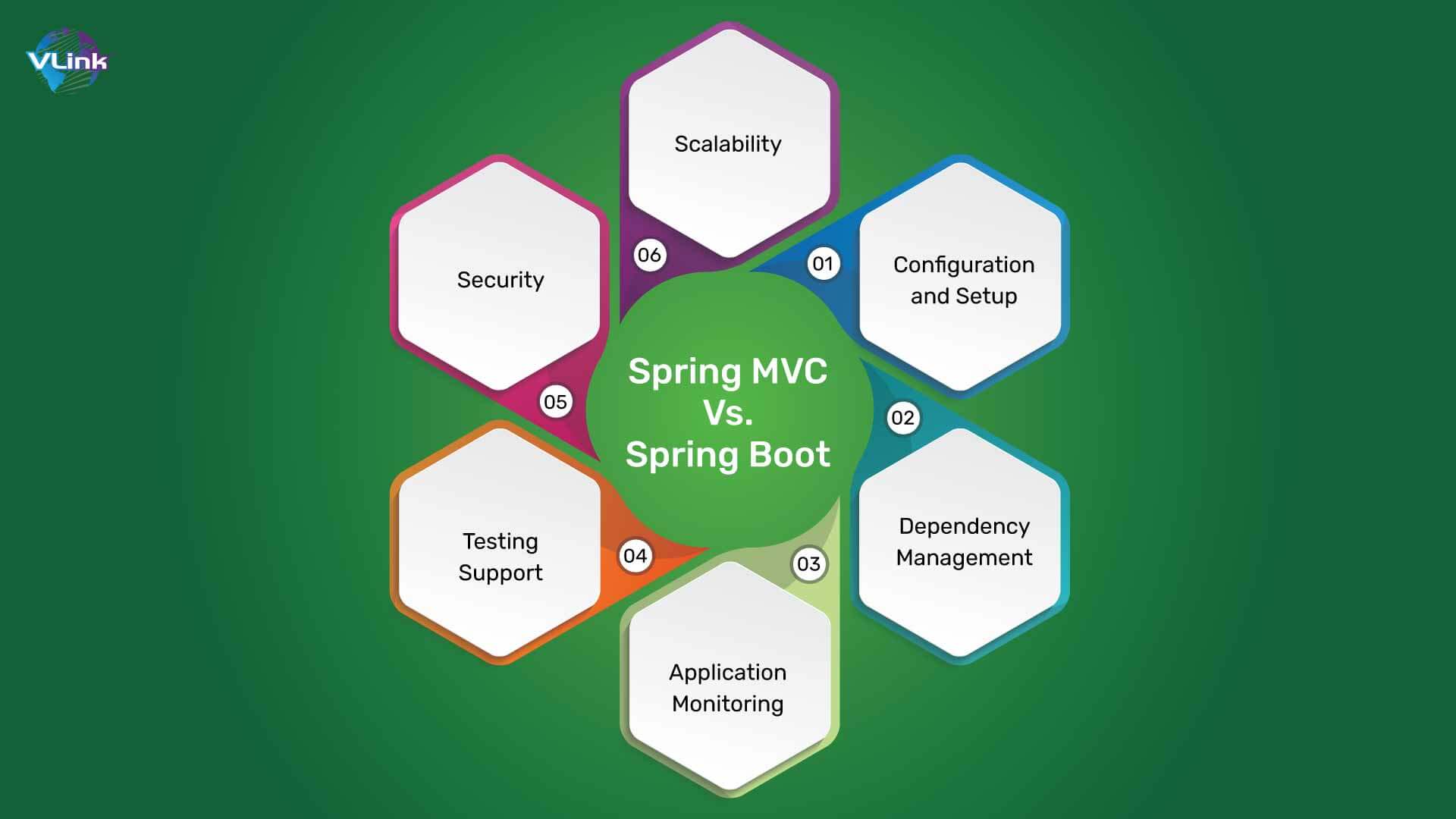
Spring MVC Vs. Spring Boot: Configuration and Setup
When it comes to easy setup and configuration, Spring Boot wins the game. It provides a rapid app development platform without any configuration, making it well-suited for small to medium-sized projects and microservices.
With the Spring Boot framework, Java developers can build apps quickly and efficiently by writing code that implements business logic.
On the other hand, Spring MVC needs manual setup and configuration. Thanks to its great customization and flexibility, this framework is more suitable for complex and large-scale enterprise projects.
Spring MVC Vs. Spring Boot: Dependency Management
Spring Boot uses a starter POM system for automatic dependency management. On the other hand, Spring MVC needs manual management of dependencies, which can lead to version conflicts if not handled correctly.
In terms of dependency management, Spring Boot wins again. With its starter dependencies features, it minimizes the risk of version conflicts.

Spring MVC Vs. Spring Boot: Application Monitoring
Spring Boot includes actuators that provide application insights and health metrics. It's ideal for production-grade applications.
Spring MVC doesn't come with an application monitoring feature. So, developers will need to configure a separate tool for application monitoring.
Spring MVC Vs. Spring Boot: Testing Support
Thanks to its MockMvc framework, Spring MVC provides extensive support for software testing services. Developers can simulate requests and responses without beginning a servlet container. They can perform different types of testing, such as unit, integration, and end-to-end, for your MVC controllers.
Spring Boot increases testing support that allows you to bootstrap the entire application context for testing. It simplifies integration testing by providing auto-configuration and sensible defaults.
Spring MVC Vs. Spring Boot: Security
Spring Security can be integrated with Spring MVC to handle authentication, authorization, and other security concerns. You need to configure security features manually, such as setting up authentication providers, defining access rules, etc.
Spring Boot simplifies security configuration by providing auto-configuration for common security scenarios. It offers starters like spring-boot-starter-security, which automatically secures your application with sensible defaults. You can customize security settings using properties or Java configurations.
Spring MVC Vs. Spring Boot: Scalability
Spring MVC applications can be scaled horizontally by deploying multiple instances behind a load balancer. However, scaling might require manual configuration and management of resources, such as connection pools, caching, etc.
Spring Boot simplifies scalability by embedding an application server (e.g., Tomcat, Jetty) and providing production-ready features out of the box. It includes metrics, health checks, externalized configuration, and more, which are essential for managing and monitoring large-scale deployments. Spring Boot applications can also be easily containerized using Docker for deployment in cloud environments.
Spring MVC Vs. Spring Boot: When to Use?
When to Use Spring MVC?
Building web applications in Java
Needing a robust, mature framework with a wide community
Requiring flexibility to integrate with other Spring modules
Utilizing a full-stack framework with support for diverse web application requirements
When to Use Spring Boot?
Rapidly prototyping or developing Spring-based applications
Preferring convention over configuration for quick setup
Building microservices or standalone applications
Needing embedded server deployment for easier distribution
Spring MVC Vs. Spring Boot: Key Differences!
Parameters | Spring MVC | Spring Boot |
Use | Idea for web app development | Idea for Spring-powered framework development |
Configurations | Manual configuration is required | Manual configuration not required |
Deployment Descriptor | Required | Not Required |
Timeline | Take More Development Time | Reduced Development Time |
Layers & Components | There are four types of presentation layers: Presentation layer, Business layer, Persistence layer, and the Database layer. | Four components in MVC such as Model, View, Controller, Front Controller, or DispatcherServlet Class. |
Dependency Management | Developers need to manage project dependencies explicitly. | Includes embedded servlet containers, eliminating manual server configuration. |
In summary, both Spring MVC and Spring Boot offer robust testing support, security features, and scalability options. However, Spring Boot provides more conveniences and opinionated defaults out of the box. So, it's the preferred choice for rapid web application development and deployment, especially in microservices architectures.
If you are looking for the best Spring Boot developers quickly for your project, contact VLink today!

Hire the top 3% of Spring Boot Developers within 48 Hours from VLink!
At VLink, we have a large network of top Spring Boot developers. They are skilled in a diverse range of additional frameworks and tools—our programmer's expertise in building dynamic web applications using String Boot, Spring Data JPA, and Spring Security. With us, you can hire the best developers for your business needs, and are committed to delivering outstanding results.
For more questions, you can contact us!







 Shivisha Patel
Shivisha Patel

















